A Surge Of Solar
The European Union has reached a significant milestone in its energy journey, with solar energy having officially surpassed coal in the region’s energy mix for 2024. This transition highlights the EU’s commitment to tackling climate change and reducing dependency on fossil fuels. With renewable sources like wind, solar, and hydropower leading the charge, this shift reflects a growing recognition of the need for cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions. In this blog, we’ll explore how the EU achieved this pivotal moment, the key drivers behind the transition, and what it means for the future of energy across Europe.
The Power Shift
The EU’s energy landscape is undergoing a transformative shift, marked by a remarkable growth in renewable energy. For the first time, solar power has overtaken coal, contributing 11% of the region’s electricity compared to coal’s 10%, as highlighted in Ember’s European Electricity Review. Renewable energy sources now account for 47% of the EU’s power mix—an impressive leap from just 34% in 2019. Conversely, fossil fuel generation has plummeted to a historic low of 29%.
The surge in solar power, which grew by an extraordinary 22% in 2024 alone, has been a key driver of this transition. With an additional 66 GW installed last year—the equivalent of 450,000 solar panels set up each day—it’s clear that Europe’s commitment to clean energy is reshaping its energy future. With experts stating that “Fossil fuels are losing their grip on EU energy,” signalling a new era of sustainable power generation.
How Renewables Are Securing Europe’s Energy Future
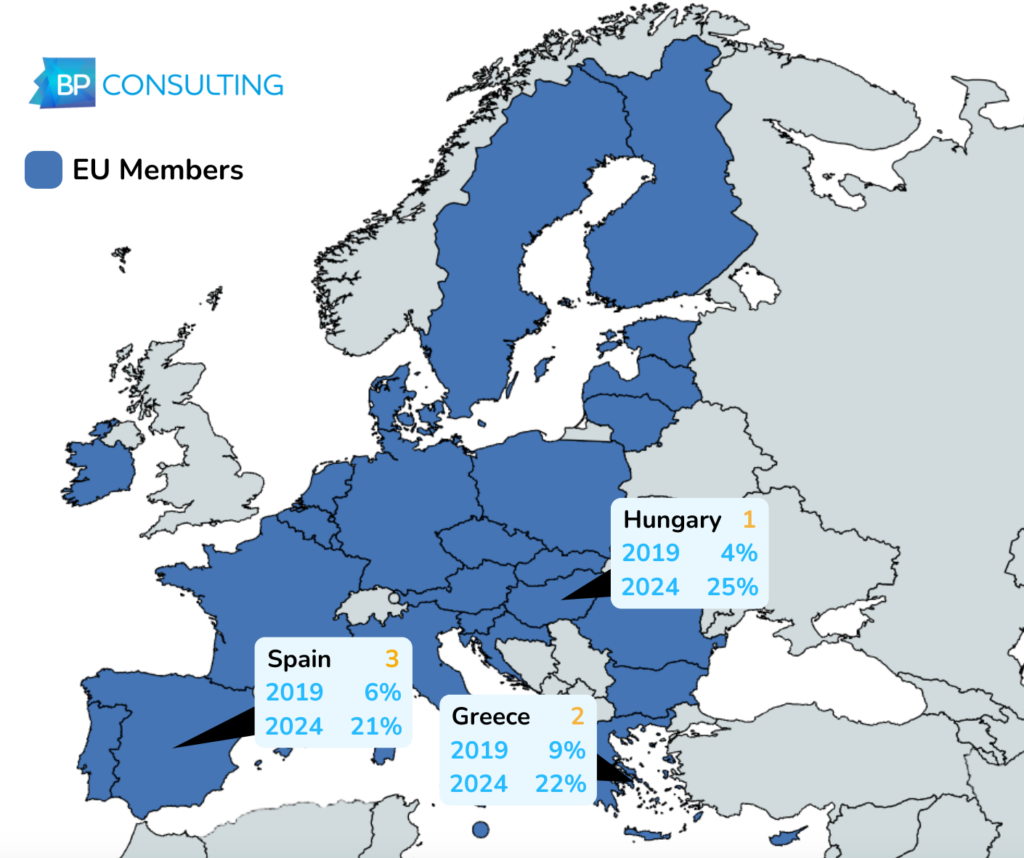
Hungary, Greece and Spain are pioneering the adoption of solar energy in Europe, with Hungary generating 25% of its power mix using solar energy, compared to only 4% in 2019. Moreover, new innovative technologies have made solar power accessible to people outside of roof or field installation. For example, Germany has seen the increased adoption of plug-in solar systems. Currently, over 700,000 homes have been fitted with what have been dubbed ‘balcony power plants’ as of October 2024, having doubled since January of that year. German analysts predict that the trend will only continue to rise.
Created Using MapChart
The rapid expansion of renewable energy has not only transformed the EU’s energy mix but also significantly reduced its reliance on imported fossil fuels. Experts predict that without the additional wind and solar capacity installed since 2019, the EU would have faced the burden of importing an extra €59 billion (£49.45 billion) worth of gas and coal—a stark reminder of the financial and energy security benefits of renewables.
However, while this progress is encouraging, experts warn that the momentum must continue. Further advancements in wind energy are critical to maintaining this trajectory, and enhancing grid flexibility will be essential to accommodate the growing share of renewable power. The EU’s success so far highlights what is possible, but the path to a fully sustainable energy system still demands continued innovation and investment.
Conclusion:
The European Union’s achievement in surpassing coal with renewable energy in its power mix is a landmark moment in its transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable future. This milestone reflects not only the region’s commitment to tackling climate change but also the tangible benefits of renewable energy, from reduced dependence on costly fossil fuel imports to enhanced energy security and economic resilience.
With countries like Hungary, Greece, and Spain leading the charge in solar adoption and innovations like Germany’s ‘balcony power plants’ making renewable energy more accessible, the EU is setting a global standard for what’s possible in the shift towards sustainability. However, this progress must act as a springboard for further action. Expanding solar and wind energy capacity as well as modernising energy grids will be crucial to maintaining this momentum and ensuring a stable, renewable-powered future.